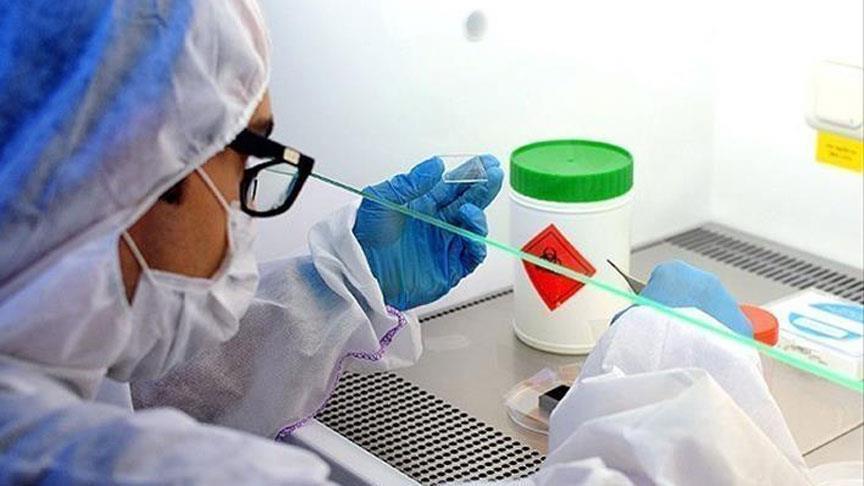
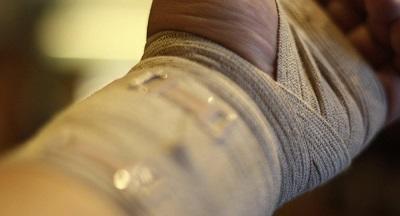
The material has a strong antibacterial effect, and can be kept on over long periods of time without needing to ever be changed, thereby accelerating skin regrowth and reducing the risk of infection.
Axar.az reports citing Sputnik.
Scientists from the Moscow-based MISiS National University of Science & Technology, the Central European Institute of Technology in Brno, the Czech Republic, and several other Russian and Czech universities have invented a new biodegradable antibacterial action field dressing
The traditional use of an antiseptic in the treatment of wounds, consisting of washing the affected area with a solution and using gauze dressing to increase the outflow of fluids, repeated several times, has saved countless lives and been instrumental in treating everything from burns and cuts to gunshot wounds and other serious injuries.
However, such treatment, particularly the use of antibiotics and the need to change the dressing regularly, has not been without its problems. For one thing, antibiotics kill not only dangerous bacteria, but useful bacteria as well. And when dressings are changed, the fragile area undergoing healing is disturbed, which can cause severe pain to patients.
Offering a solution, Russian and Czech scientists say they have come up with a biocompatible dressing material which can act locally on the area of inflammation, and, just as significantly, does not require changing. As they slowly release their antibiotic, the dressings gradually dissolve on the skin. A new one can be put on over top of the old one, if necessary, without removing it.
Scientists performed experiments using three strains of E. coli bacteria, with the strains showing varying levels of resistance to the antibiotics, but nonetheless combatted against effectively by the dressing.
According to the scientists, their new material is potentially applicable not only for treatment to heal skin, but to treat inflammatory bone diseases such as osteoporosis and osteomyelitis as well.